Are you interested in our solutions? Then write us a message. Our sales team will be happy to help you.
Start enquiryIn order to drive autonomously and safely, self-driving cars always need to be focused on their surroundings and their interiors with the aid of their sensors (“Sense”).
Cameras, radar, ultrasonic and lidar sensors are the eyes and ears of an automated car and supply all the information required by the vehicle to perceive its entire surroundings. Additional sensors are even aligned inward into the passenger compartment, enabling the system to make autonomous decisions as to whether the driver is capable of taking control of the vehicle again if necessary.
But automated cars are aware of even more than their immediate surroundings: using up-to-date, high-resolution digital maps and connected real-time data from the cloud, the vehicle can also access external information such as traffic or weather data. Taken together, the vehicle therefore avails of a solid basis of information for the smart vehicle computer, which uses it for exact calculations. For a safe and relaxing drive in a self-driving car.
Using sensory data of the car’s surroundings, automated vehicles can detect critical situations faster and avoid them better than human drivers.
Automated vehicles can detect monotonous situations like traffic jams and take over the driving task. Thus, drivers reach their destination more relaxed.

The front camera detects and categorizes objects and other road users, traffic signs as well as road markings robustly and reliably and ensures a holistic understanding of the scene. Near-range cameras additionally generate a three-dimensional image of the immediate vehicle‘s surroundings.
Ultrasonic sensors emit short ultrasonic pulses that are reflected by obstacles (echo sounder principle). This enables a very fast and robust object detection. Due to their rather small range, the sensors are used in close range, especially for parking.
The front, rear or side mounted radar uses radio waves to detect the precise position, relative speed and direction of movement of objects in almost all weather conditions, in darkness and in tunnels with just one measurement based on the time it takes for the waves to return.
One of the key requirements for automated driving is reliable and precise perception of the vehicle’s surroundings. Since the vehicle has to move autonomously in real traffic, it must be able to detect and localize all relevant road users in the surrounding area (360 degrees). This involves multiple sensors using various surveying principles to monitor each area of the vehicle’s surroundings. Most of the sensors required for these tasks are already in production today.
To obtain useful data from at least two sensors at all times, several different components such as radar, video, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors must work together. Bosch has the required expertise in all of these sensor technologies to meet the demands of surround sensing and to ensure that the sensors work together optimally. Fusing data from the individual sensors broadens the measuring range and increases the reliability and accuracy of the measurements.
The fusion of radar, camera, and lidar data allows even thin silhouettes and plastic trim to be detected more reliably. Speed limits detected by the camera are incorporated into the driving strategy by the radar sensors. And fusing data from ultrasonic sensors and the near-range camera not only enables more complex parking maneuvers, it also makes them simpler and safer.
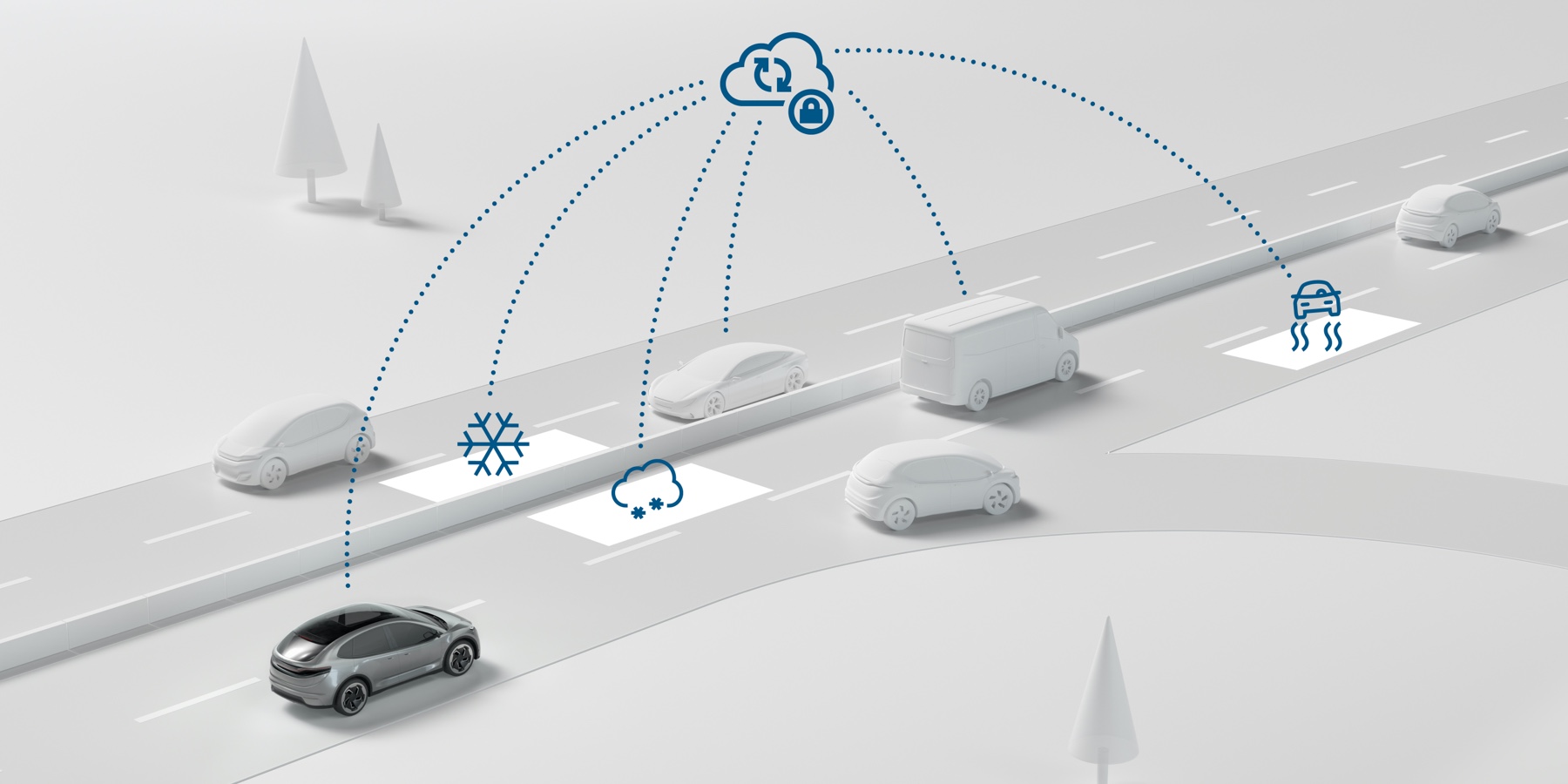
A basic requirement for highly and fully automated driving is represented by vehicle localization which must be both exact and constantly available. A single sensor is unable to fulfill these requirements which is why a combination of surround sensors with satellite navigation and correction service as well as inertial sensors and a digital map is used. High-definition digital maps are used for this purpose which contain far more layers of information than the maps for standard sat-nav devices.
They also support the automated vehicle in planning individual driving maneuvers, e. g. whether the vehicle should change lanes or not. Through connectivity with the cloud, the data contained in the maps are constantly updated enabling inclusion of dynamic factors in travel plans. For the so-called road signature, Bosch has developed a pioneering solution for creating key parts of high-definition maps using vehicles’ radar and video sensors, literally as they drive by.
Are you interested in our solutions? Then write us a message. Our sales team will be happy to help you.
Start enquiry
